Take MAP® & be a Healthy Champion!
- Provides better and faster muscle mass growth, strength, and endurance;
- Provides a better and faster muscle recovery; and
- Provides a lighter and shorter digestion;
Take MAP® & go the extra mile!
What is MAP Master Amino Acid Pattern®?
MAP Master Amino Acid Pattern® is the unparalleled, unique, proprietary amino acid formula discovered and patented by the International Nutrition Research Center, a leading American research institution in the field of human nutrition led by Prof. Dr. Maurizio Lucà-Moretti®.
In recognition of MAP Master Amino Acid Pattern®’s safety, originality, and unprecedented nutritional effectiveness, numerous patents have been granted by the following thirty countries namely, the United States, Canada, Japan, Austria, Belgium, Bulgaria, Croatia, Republic of Cyprus, Czech Republic, Denmark, Estonia, Finland, France, Germany, Greece, Hungary, Ireland, Italy, Latvia, Lithuania, Luxembourg, Malta, Netherlands, Poland, Portugal, Romania, Slovakia, Slovenia, Spain, and Sweden.
Considering the scientific evidence previously described, it can be concluded, that this is the highest number of patents granted by the highest number of nations, in recognition of MAP Master Amino Acid Pattern® originality and unprecedented nutritional effectiveness, in comparison to any dietary protein, protein supplement or amino acid formula.
Since 1992, the scientific evidence proceeding from forty-five published scientific clinical studies1-45, performed on human subjects, has shown and confirmed that the use of MAP Master Amino Acid Pattern® is:
- The most nutritious and the most health-preserving.
- The only one to be digested in less than 23 min. That is, the shortest digestion time ever.
- The only one that releases, during digestion, only 1% of nitrogen catabolites. That is, the lowest amount of metabolic toxic waste ever released.
- The only one that provides only 0.04 kcal/g. That is, the lowest amount of kcal/g ever provided.
In comparison to any dietary protein, protein supplement, or amino acid formula.
Take MAP® & preserve your health.
Why is MAP Master Amino Acid Pattern® the most nutritious in comparison to any dietary protein, protein supplement, or amino acid formula?
The scientific evidence obtained from forty-five published comparative clinical studies performed in human subjects1-45 has shown and confirmed that the use of MAP Master Amino Acid Pattern® is:
- the most nutritious and the most health-preserving,
in comparison to any dietary protein, protein supplement, or amino acid formula.
To illustrate:
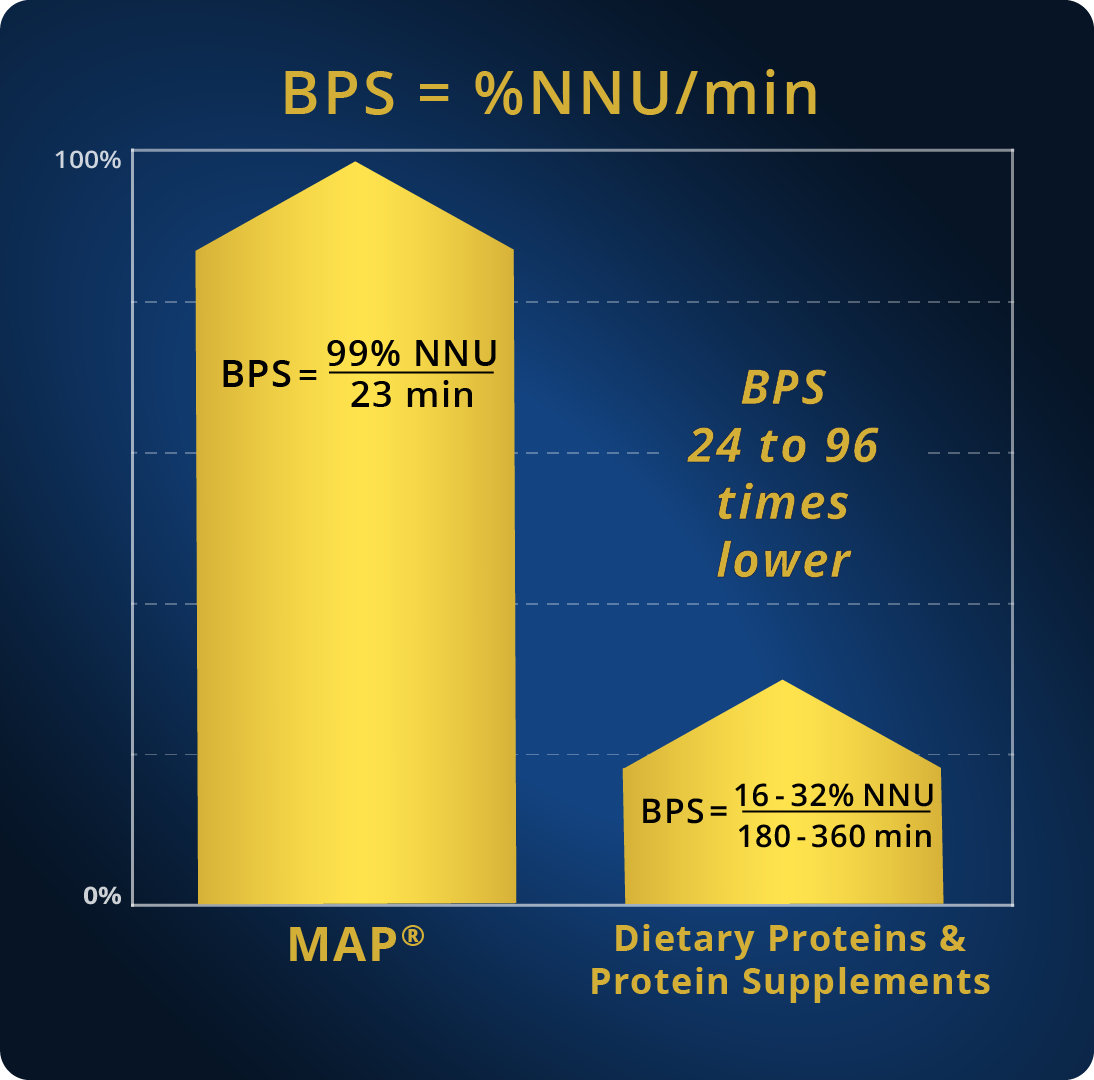
1. MAP Master Amino Acid Pattern® provides a unique, unprecedented, Body Protein Synthesis (BPS = 99%NNU/23min), namely the highest in comparison to any dietary protein, protein supplement or amino acid formula.
Comparative clinical Net Nitrogen Utilization (NNU) studies, performed in human subjects1-4, have shown and confirmed that the use of MAP Master Amino Acid Pattern® provides an unprecedented and unique BPS = 99%NNU/23 min*. On the contrary, dietary proteins provide a BPS of 16-32% NNU/180-360 min. That is, a BPS 24 to 96 times lower compared to that of MAP Master Amino Acid Pattern®. As a result, it can be concluded that MAP Master Amino Acid Pattern® provides a BPS that is 24 to 96 times higher in comparison to that provided by any dietary protein, protein supplement, or amino acid formula.
2. MAP Master Amino Acid Pattern® requires less than 23 minutes to be digested. That is, the shortest digestion time required in comparison to any dietary protein or protein supplement.
Comparative clinical studies performed on human subjects1-4 have shown that MAP Master Amino Acid Pattern® requires less than 23 minutes to be digested. On the contrary, dietary proteins require a digestion time of 180 to 360 minutes (3 to 6 hours). That is, a digestion time 6 to 12 times longer in comparison to that required by MAP Master Amino Acid Pattern®. As a result, it can be concluded that MAP Master Amino Acid Pattern® requires a digestion time 6 to 12 times shorter in comparison to any dietary protein, protein supplement or amino acid formula.

Why is the use of MAP Master Amino Acid Pattern® the most health-preserving in comparison to any dietary protein, protein supplement, or amino acid formula?
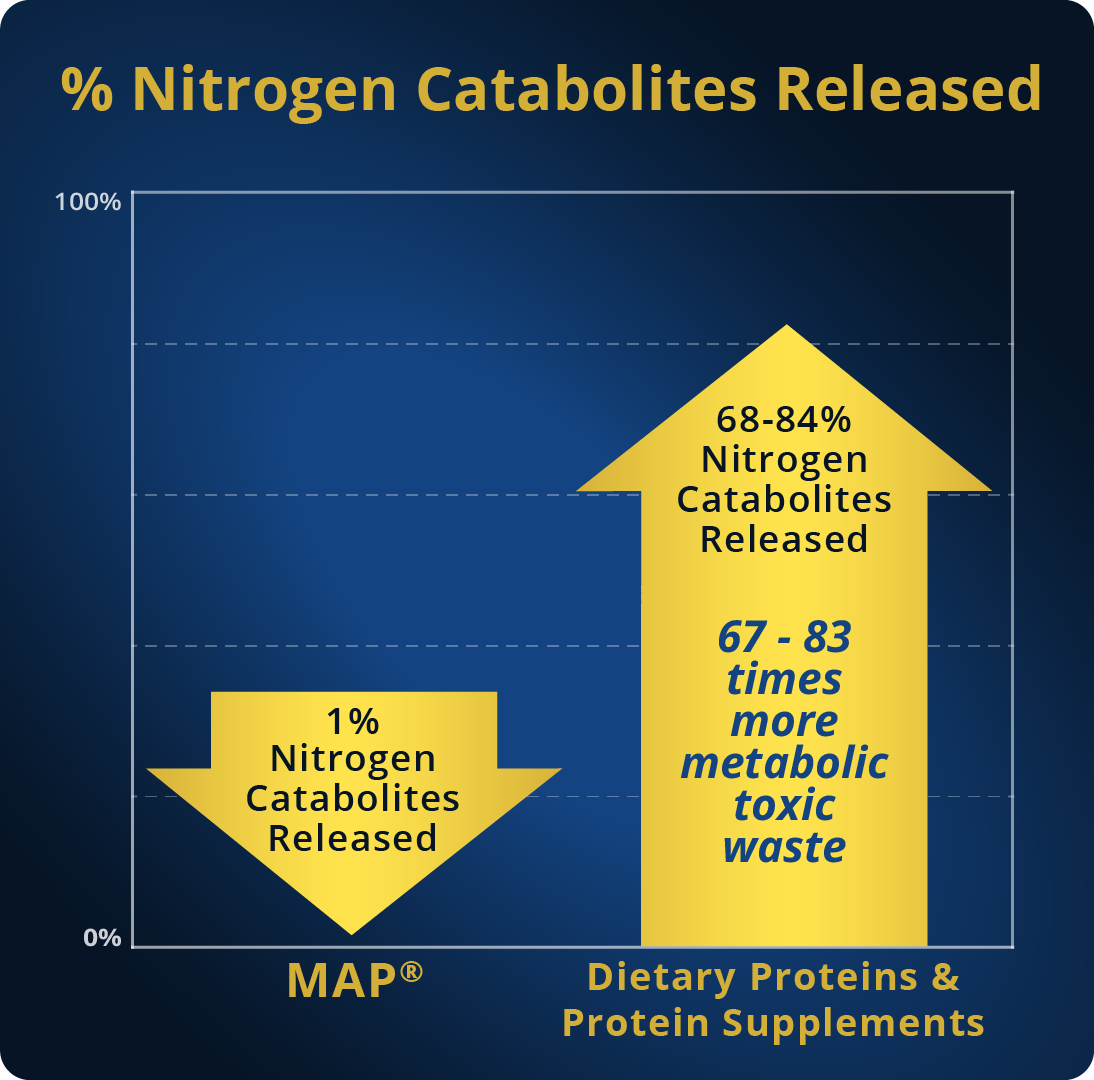
3. The use of MAP Master Amino Acid Pattern® releases, while being digested, only 1% nitrogen catabolites, namely metabolic toxic waste. That is, the lowest amount of nitrogen catabolites ever released, in comparison to any dietary protein, protein supplement, or amino acid formula.
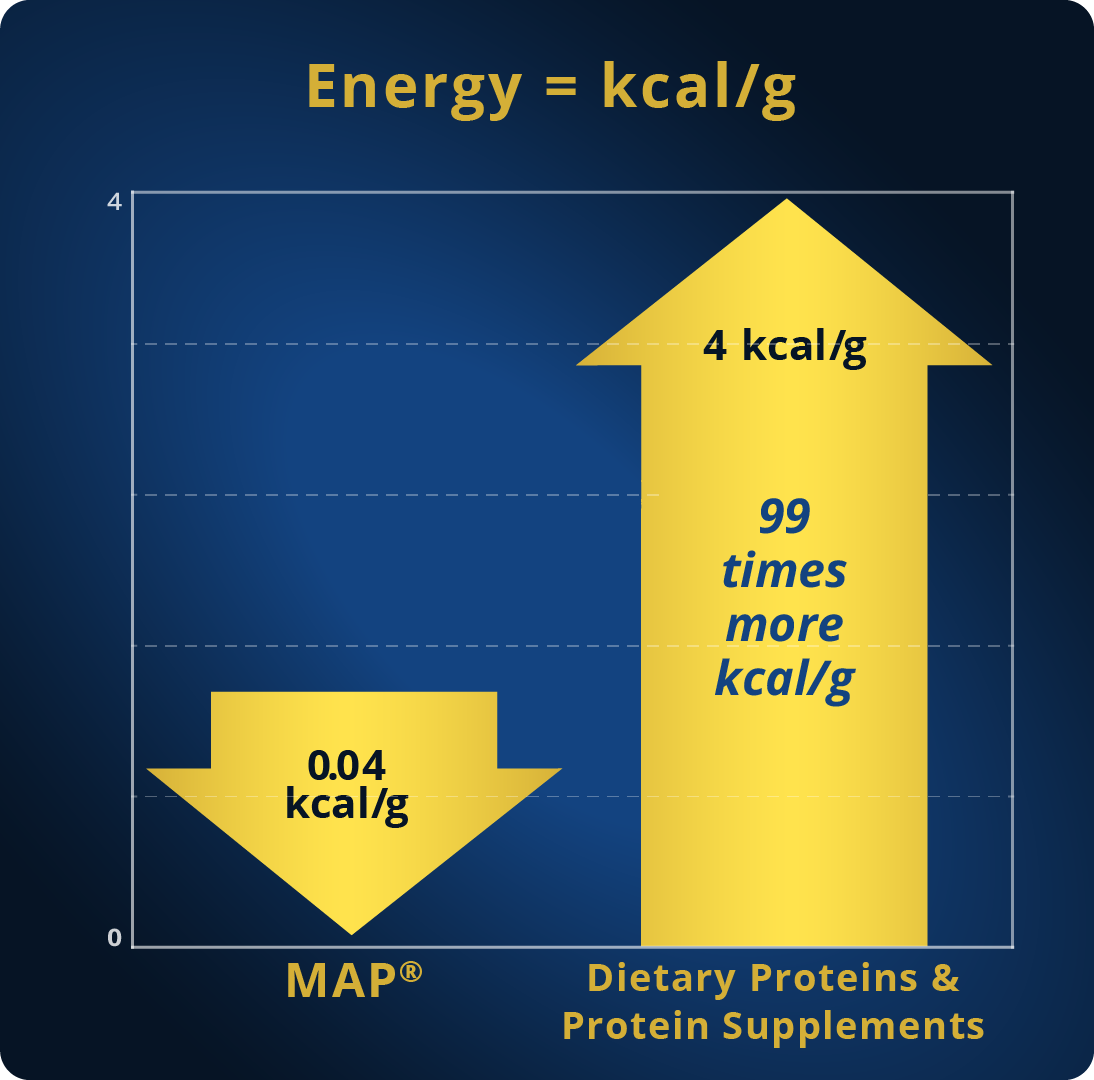
4. The use of MAP Master Amino Acid Pattern® provides only 0.04 kcal/g. That is, the lowest amount of kcal/g in comparison to that provided by any dietary protein, protein supplement, or amino acid formula.
5. The fifth and last unique characteristic of MAP Master Amino Acid Pattern® originates from the cumulative effects of its, previously described, four unique characteristics. As a result, the use of MAP Master Amino Acid Pattern®, in substitution for dietary proteins, protein supplements, or amino acid formulas can significantly reduce renal, hepatic, pancreatic, digestive, cardiovascular, and/or respiratory load in comparison to any dietary protein, protein supplement, or amino acid formula.
CONCLUSIONS
The scientific evidence obtained from the publication of forty-five comparative clinical studies1-45, conducted in human subjects, while ingesting, MAP Master Amino Acid Pattern®, as a partial or total substitute for dietary proteins, has shown and confirmed that its use is:
- the most nutritious and the most health-preserving,
in comparison to any dietary protein, protein supplement or amino acid formula.
| Characteristics | MAP Master Amino Acid Pattern® | Dietary Proteins From Vegetable Origin | Dietary Proteins From Animal Origin | Protein Supplements From Either Animal or Vegetable Origin (e.g. such as whey, casein or soy) | Amino Acid Supplements Not Containing the Eight Essential Amino Acids (e.g. branched amino acids) | Amino Acid Supplements Containing All Eight Essential Amino Acids (however, proceeding from hydrolyzed proteins such as whey, casein or soy) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Net Nitrogen Utilization (NNU%) | 99% NNU | 16% NNU (average) | 32% NNU (average) | 16% NNU (average) | 0% NNU | 16% NNU (average) |
| Digestion Time | 23 min | 180-360 min (6-12 times longer) | 180-360 min (6-12 times longer) | 180-360 min (6-12 times longer) | 120-180 min (4-6 times longer) | 180-360 min (6-12 times longer) |
| BPS=(NNU%/min) | BPS=99% NNU/ 23 min | 48-96 times lower | 24-48 times lower | 48-96 times lower | 99 times lower | 48-96 times lower |
| Nitrogen Catabolites (%) Released | 1% | 84% (average) | 68% (average) | 84% (average) | 100% (average) | 84% (average) |
| Energy Input (kcal/g) | 0.04 kcal/g | 4 kcal/g | 4 kcal/g | 4 kcal/g | 4 kcal/g | 4 kcal/g |
| Fecal residue | Absent | Present | Present | Present | Absent | Variable |
| Contraindications | None | Renal Failure or Hepatic Failure | Renal Failure or Hepatic Failure | Renal Failure or Hepatic Failure | Renal Failure or Hepatic Failure | Renal Failure or Hepatic Failure |
| Adverse Reactions | None | Food Sensitivities | Food Sensitivities | Food Sensitivities | Food Sensitivities | Food Sensitivities |
| Refrigeration | NOT Required | Required | Required | Required | Variable | Variable |
SCIENTIFIC REFERENCES RELATED TO MAP MASTER AMINO ACID PATTERN®
- Lucà-Moretti M. Comparative study of subjects’ Net Nitrogen Utilization (NNU) while receiving SON, a nutritional amino acid formula, or high biological value egg protein, or egg protein amino acid formula. JIMHA; 1:33-42, 1992.
- Lucà-Moretti M. Comparative study of subjects’ Net Nitrogen Utilization (NNU) while receiving SON, or egg protein or its protein amino acid formula. Advances in Therapy; 5:280-89, 1992.
- Lucà-Moretti M. Comparative study of subjects’ Net Nitrogen Utilization (NNU) while receiving bovine milk or soybean flour with or without SON nutrification. JIMHA; 1:43-54, 1992.
- Lucà-Moretti M. Comparative study of subjects’ Net Nitrogen Utilization (NNU) while receiving bovine milk or soybean flour with or without SON nutrification. Advances in Therapy; 5:290-301, 1992.
- Lucà-Moretti M., Grandi, A. The Malnutrition Treatment and Prevention Project. JIMHA; 2:20-26, 1993.
- Lucà-Moretti M., Grandi, A. Comparative Study of Subjects’ Weight Loss while receiving Very Low Calorie Diets consisting of SON, SON-Nutrified Dried Bovine Skim Milk, or Dried Bovine Skim milk provided in the required amounts to achieve Zero Nitrogen Balance. JIMHA; 2:39-48, 1993.
- Tamburlin N. L’importanza innovativa nell’uso del MAP per il controllo biologico del peso. La Medicina Biologica; 1:4-10, 1997.
- Lucà-Moretti M. Ensayo Comparativo sobre el MAP: el perfil ideal de aminoácidos esenciales para la nutrición humana, International Journal for Biomedical Research and Therapy; 4:9-14, 1997.
- Lucà-Moretti M. A Comparative, Double-blind, Triple Crossover Net Nitrogen Utilization Study Confirms the Discovery of the Master Amino Acid Pattern. Annals of the Royal National Academy of Medicine of Spain, Madrid; Vol. CXV: 397-416, 1998.
- Lucà-Moretti M. A Comparative, Double-blind, Triple Crossover Net Nitrogen Utilization Study Confirms the Discovery of the Master Amino Acid Pattern. Annals of the Royal Academy of Medicine of Zaragoza. Zaragoza; LXXII, 1998.
- Lucà-Moretti M. The International Nutrition Research Center Overweight Management Program. The Library of Congress, USA 1999.
- Fidone B. Rettocolite ulcerosa idiopatica: possibilita con MAP (SON Formula). La Medicina Biologica; 3:8-11, 1999.
- Sanseverino E. R. Vantaggi dell’utilizzo del MAP in eta’geriatrica. La Medicina Biologica; 3:17-19, 1999.
- Lucà-Moretti M. Programma di trattamento e prevenzione della malnutrizione. La Medicina Biologica; 3:35-38, 1999.
- Costanzo S. Nuova opportunita nella nutrizione delle popolazioni in situazioni di emergenza. La Medicina Biologica; 3:39-42, 1999.
- Mariani E., Vender G., Arrigotti E., Ferrario M., Rovelli E. Variazione di alcuni parametri antropometrici e fisiologici in una marciatrice cinquantenne prima e dopo l’attraversamento in solitaria del deserto cinese. La Medicina Biologica; 3:20-25, 1999.
- Tamburlin N. Trattamento ambulatoriale di pazienti con insufficienza renale cronica. La Medicina Biologica; 3:12-16, 1999.
- Muratori G. Sovrappeso e patologia articolare: SON Formula come terapia dimagrante ed antalgica un’ipotesi di lavoro. La Medicina Biologica; 17-20, 1999.
- Montilla C. Studio comparativo con e senza somministrazione di SON FORMULA® in soggetti affetti da anemia sideropenica sotto trattamento convenzionale. La Medicina Biologica; 3:2-7, 1999.
- Riccobene F. Impiego della neuralterapia sec. Huneke in casi di ritensione idrosalina non responsivi alla terapia diuretica in corso di dieta dimagrante con SON Formula. La Medicina Biologica; 3:48-52, 1999.
- Hermann G.F. Le intolleranze alimentari. La Medicina Biologica; 3:3-7, 2000.
- Corgna M. Pnei e patologie psiconutrizionali in omotossicologia. Il trattamento delle sindromi bulimiche. La Medicina Biologica; 3:8-16, 2000.
- Tamburlin N. Il SON Formula come opportunita nella gestione delle intolleranzealimentari. La Medicina Biologica; 3:24-29, 2000.
- Di Tullio G. Biotipologia del comportamento alimentare e utilizzo del SON Formula. La Medicina Biologica; 3:34-37, 2000.
- Ivaldi G.P. Esperienza nutrizionale in pazienti con insufficienza respiratoria. La Medicina Biologica; 3:49-54, 2000.
- Bufalini L. Nutrizione biologica integrata con SON Formula in pazienti affetti da sclerosi multipla. La Medicina Biologica; 3:55-61, 2000.
- D’Andrea G. Terapia delle obesitá: Studio comparativo di 10 casi clinici trattati con MAP (Son Formula™) e terapia omotossicologica versus Orlistat (Xenical 120mg Roche). La Medicina Biologica; 3:5-9, 2001.
- Di Tullio G. La Malattia asmatica: il ruolo della nutrizione biologica. La Medicina Biologica; 3:15-19, 2001.
- Del Prete M. Le malattie infiammatorie intestinali: importanza diagnostica e terapeutica del MAP. La Medicina Biologica; 3:20-26, 2001.
- Mariani M.M. Utilizzo del MAP (Master Amino acid Pattern) nel Programma “Quattro D” nell’insufficienza venosa cronica. La Medicina Biologica; 3:33-40, 2001.
- Falcone S., Cornoldi A., Brandetti F., Pili M., Badiali M., Spera G., Lubrano C. Integrazione con SON Formula in pazienti grandi obesi operati di by-pass biliointestinale presso il Policlinico Umberto I di Roma. La Medicina Biologica; 3:46-52, 2001.
- Fidone B. Nutrizione biologica integrata con SON Formula in pazienti affetti da insufficienza cardiaca. La Medicina Biologica; 3:53-66, 2001.
- Bufalini L. Rieducazione nutrizionale e terapia omotossicologica in pazienti anoressiche amenorroiche. La Medicina Biologica; 3:67-71, 2001.
- Polito A. Encefalopatia portosistemica in fase terminale in paziente cirrotico: Terapia con SON Formula. La Medicina Biologica; 49-50, 2001.
- Tamburlin N. Correlazioni tra micosi cutanuee ed intolleranze alimentari. La Medicina Biologica; 67-75, 2001.
- De Cristofano C., Giordano F. Terapia omeopatica integrata in un caso di cirrosi epatica scompensata. La Medicina Biologica; 51-52, 2002.
- Lucà-Moretti, M., Grandi A., Lucà E., Mariani E., Vender G., Arrigotti E., Ferrario M., Rovelli E. Comparative Results Between Two Groups of Track and Field Athletes with or without the use of Master Amino Acids Pattern® as protein substitute. Advances in Therapy; 4:195-202, 2003.
- Lucà-Moretti, M., Grandi A., Lucà E., Mariani E., Vender G., Arrigotti E., Ferrario M., Rovelli E Results of taking Master Amino Acids Pattern® as a sole and total substitute of dietary proteins in an athlete during a desert crossing. Advances in Therapy; 4:203-210, 2003.
- Lucà-Moretti, M., Grandi A., Lucà E., Muratori G., Nofroni M.G., Mucci M.P., Gambetta P., Stimolo R., Drago P., Giudice G., Tamburlin N., Karbalay M., Valente C., Moras G. Master Amino Acids Pattern® as sole and total substitute for dietary proteins during a weight loss diet to achieve the body’s Nitrogen Balance equilibrium. Advances in Therapy; 5:270-281, 2003.
- Lucà-Moretti, M., Grandi A., Lucà E., Muratori G., Nofroni M.G., Mucci M.P., Gambetta P., Stimolo R., Drago P., Giudice G., Tamburlin N. Master Amino Acids Pattern® as substitute for dietary proteins during a weight loss diet to achieve the body’s Nitrogen Balance equilibrium with essentially no calories. Advances in Therapy; 5:282-291, 2003.
- Ripa S. Il programma SON Formula. Argomenti di medicina estetica biologica; Guna Ed., Milano, 2004.
- Marucci S. Linfedema ereditario e malassorbimento proteico con deficit secondario di HGH. La Medicina Biologica; 21-25, 2004.
- Turco L. Rete ippocampale come modello della late-life: approccio farmacologico di regolazione nel senex. La Medicina Biologica; 55-59, 2004.
- Penco P., Frigerio F., Orlandi S., Molinari R. Progetto SET/K13: Rilievi su un caso estremo. La Medicina Biologica; 15-22, 2006.
- Lanza A. Intrauterine Growth Restriction prevention by Master Amino Acid Pattern. Atti del XXI Congresso Nazionale di Omeopatia, Omotossicologia e Medicina Biologica. La Medicina Biologica; 4:35-43, 2006.

